|
VC++
Example:
Draw Emboss text and other Shadow shape on your bitmap
|
| |
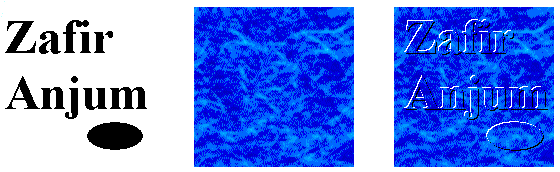
Zafir Anjum
This is best explained
with pictures. The left most image
is some text and a
simple shape. The image
in the middle is the bitmap
on which we want to emboss
the first image. The
result is shown in the third image.
So, this topic will basically give you the code to achieve
this result. The code also allows you to get a sunk-in
effect rather than a raised effect.
The basic idea behind the Emboss()
function given below is very simple. It creates a
monochrome bitmap that
represents the edges that need to be highlighted and it
creates another monochrome bitmap of the edges that need a
shadow. These two bitmaps are then used to draw
the highlight and the shadow.
The detail, however, is a little bit more involved. Let's
cover the main steps, one at a time.
The raised and sunken
effect is merely achieved by using a lighter color on one
edge and a darker color on the other edge. If we use a
light color for the edges towards the top left then we get
a raised effect. Conversely, if we use a dark color for
the edges towareds the top left then we get a sunken
effect. So, if the function is called with the bRaised
flag set to false, then we simply swap the highlight and
the shadow color to get a sunken effect.
The next major step is
creating the highlight bitmap. We use a monochrome bitmap
for this purpose since a monochrome bitmap has just a
background and a foreground and makes our tucancode.net simpler.
- We set the entire
bitmap to white using PatBlt(). White is the
background color in monochrome bitmap. This assures
that any portion of the bitmap not drawn to will have
the background color.
- Next we copy the source
image to the highlight bitmap using BitBlt() to get a
monochrome image. We copy the image 1 pixel closer to
the top-left corner. Our purpose is to get a one pixel
wide highlight edge for all the edges towards the
top-left corner.
- This is the important
step. We use another BitBlt() to remove all the extra
edges in the highlight bitmap. We use the MERGEPAINT
raster operation for this. What MERGEPAINT does is, it
converts all the pixels in the destination bitmap (the
highlight bitmap) corresponding to a foreground pixel
in the source to white (the background color). Any
pixel in the destination bitmap is unchanged when the
corresponding pixel in the source is a background
pixel. This explanation applies because we are dealing
with a monochrome bitmap as the destination bitmap.
Note that we do not use an offset for this operation,
e.i. the destination x and y coordinates as well as
the source x and y coordinates are all zero. The net
effect of step 2 and 3 is that we get a single pixel
wide line for all the edges that need to be
highlighted.
In a similar manner, we
create the shadow bitmap.
We then copy the the background bitmap onto the result
bitmap and then draw
the highlight edges using the highlight color and the shadow
edges using the shadow
color. To copy the highlight and shadow colors we use the
raster op-code 0x00B8074A. This is also represented as
PSDPxax which is reverse polish notation for
((P^D)&S)^P, where P,S and D stand for pattern brush,
source and destination. This probably still doesn't make a
lot of sense so I'll just tell you what the effect of this
raster operation is. Given that the text color is black
and the background color is white - we set this up by
calling SetBkColor() and SetTextColor() - the result of
the raster operation is that for every black pixel ( the
foreground color in a monochrome bitmap ) in the source
the brush color is copied to the destination. You will
note that we do select an appropriate brush before the
call to BitBlt().
//prototype for default arguments - include this in your header file
HBITMAP Emboss( HBITMAP hBitmap, HBITMAP hbmBackGnd, HPALETTE hPal, BOOL bRaised = TRUE,
int xDest = 0, int yDest = 0,
COLORREF clrHighlight = GetSysColor( COLOR_BTNHIGHLIGHT ),
COLORREF clrShadow = GetSysColor( COLOR_BTNSHADOW ));
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Emboss - Creates a 3D embossed effect
// Returns - A new bitmap containing the resulting effect
// hBitmap - Bitmap that contains the basic text & shapes
// hbmBackGnd - Contains the color image
// hPal - Handle of palette associated with hbmBackGnd
// bRaised - True if raised effect is desired. False for sunken effect
// xDest - x coordinate - used to offset hBitmap
// yDest - y coordinate - used to offset hBitmap
// clrHightlight - Color used for the highlight edge
// clrShadow - Color used for the shadow
//
// Note - 1. Neither of the bitmap handles passed in should be selected
// in a device context.
// 2. The pixel at 0,0 in hBitmap is considered the background color
//
HBITMAP Emboss( HBITMAP hBitmap, HBITMAP hbmBackGnd, HPALETTE hPal,
BOOL bRaised, int xDest, int yDest,
COLORREF clrHighlight, COLORREF clrShadow )
{
const DWORD PSDPxax = 0x00B8074A;
BITMAP bmInfo ;
HBITMAP hbmOld, hbmShadow, hbmHighlight, hbmResult, hbmOldMem ;
HBRUSH hbrPat ;
HDC hDC, hColorDC, hMonoDC, hMemDC ;
if( !bRaised )
{
// Swap the highlight and shadow color
COLORREF clrTemp = clrShadow;
clrShadow = clrHighlight;
clrHighlight = clrTemp;
}
// We create two monochrome bitmaps. One of them will contain the
// highlighted edge and the other will contain the shadow. These
// bitmaps are then used to paint the highlight and shadow on the
// background image.
hbmResult = NULL ;
hDC = GetDC( NULL ) ;
// Create a compatible DCs
hMemDC = ::CreateCompatibleDC( hDC );
hMonoDC = CreateCompatibleDC( hDC );
hColorDC = CreateCompatibleDC( hDC );
if( hMemDC == NULL || hMonoDC == NULL || hColorDC == NULL )
{
if( hMemDC ) DeleteDC( hMemDC );
if( hMonoDC ) DeleteDC( hMonoDC );
if( hColorDC ) DeleteDC( hColorDC );
return NULL;
}
// Select the background image into memory DC so that we can draw it
hbmOldMem = (HBITMAP)::SelectObject( hMemDC, hbmBackGnd );
// Get dimensions of the background image
BITMAP bm;
::GetObject( hbmBackGnd, sizeof( bm ), &bm );
// Create the monochrome and compatible color bitmaps
GetObject( hBitmap, sizeof( BITMAP ), (LPSTR) &bmInfo ) ;
hbmShadow =
CreateBitmap( bmInfo.bmWidth, bmInfo.bmHeight, 1, 1, NULL ) ;
hbmHighlight =
CreateBitmap( bmInfo.bmWidth, bmInfo.bmHeight, 1, 1, NULL ) ;
hbmResult =
CreateCompatibleBitmap( hDC, bm.bmWidth, bm.bmHeight ) ;
hbmOld = (HBITMAP)SelectObject( hColorDC, hBitmap ) ;
// Set background color of bitmap for mono conversion
// We assume that the pixel in the top left corner has the background color
SetBkColor( hColorDC, GetPixel( hColorDC, 0, 0 ) ) ;
// Create the highlight bitmap.
hbmHighlight = (HBITMAP)SelectObject( hMonoDC, (HGDIOBJ) hbmHighlight ) ;
PatBlt( hMonoDC, 0, 0, bmInfo.bmWidth, bmInfo.bmHeight, WHITENESS ) ;
BitBlt( hMonoDC, 0, 0, bmInfo.bmWidth - 1, bmInfo.bmHeight - 1,
hColorDC, 1, 1, SRCCOPY ) ;
BitBlt( hMonoDC, 0, 0, bmInfo.bmWidth, bmInfo.bmHeight,
hColorDC, 0, 0, MERGEPAINT ) ;
hbmHighlight = (HBITMAP)SelectObject( hMonoDC, (HGDIOBJ) hbmHighlight ) ;
// create the shadow bitmap
hbmShadow = (HBITMAP)SelectObject( hMonoDC, (HGDIOBJ) hbmShadow ) ;
PatBlt( hMonoDC, 0, 0, bmInfo.bmWidth, bmInfo.bmHeight, WHITENESS ) ;
BitBlt( hMonoDC, 1, 1, bmInfo.bmWidth-1, bmInfo.bmHeight-1,
hColorDC, 0, 0, SRCCOPY ) ;
BitBlt( hMonoDC, 0, 0, bmInfo.bmWidth, bmInfo.bmHeight,
hColorDC, 0, 0, MERGEPAINT ) ;
hbmShadow = (HBITMAP)SelectObject( hMonoDC, (HGDIOBJ) hbmShadow ) ;
// Now let's start working on the final image
SelectObject( hColorDC, hbmResult ) ;
// Select and realize the palette if one is supplied
if( hPal && GetDeviceCaps(hDC, RASTERCAPS) & RC_PALETTE )
{
::SelectPalette( hColorDC, hPal, FALSE );
::RealizePalette(hColorDC);
}
// Draw the background image
BitBlt(hColorDC, 0, 0, bm.bmWidth, bm.bmHeight, hMemDC, 0, 0,SRCCOPY);
// Restore the old bitmap in the hMemDC
::SelectObject( hMemDC, hbmOldMem );
// Set the background and foreground color for the raster operations
SetBkColor( hColorDC, RGB(255,255,255) ) ;
SetTextColor( hColorDC, RGB(0,0,0) ) ;
// blt the highlight edge
hbrPat = CreateSolidBrush( clrHighlight ) ;
hbrPat = (HBRUSH)SelectObject( hColorDC, hbrPat ) ;
hbmHighlight = (HBITMAP)SelectObject( hMonoDC, (HGDIOBJ) hbmHighlight ) ;
BitBlt( hColorDC, xDest, yDest, bmInfo.bmWidth, bmInfo.bmHeight,
hMonoDC, 0, 0, PSDPxax ) ;
DeleteObject( SelectObject( hColorDC, hbrPat ) ) ;
hbmHighlight = (HBITMAP)SelectObject( hMonoDC, (HGDIOBJ) hbmHighlight ) ;
// blt the shadow edge
hbrPat = CreateSolidBrush( clrShadow ) ;
hbrPat = (HBRUSH)SelectObject( hColorDC, hbrPat ) ;
hbmShadow = (HBITMAP)SelectObject( hMonoDC, (HGDIOBJ) hbmShadow ) ;
BitBlt( hColorDC, xDest, yDest, bmInfo.bmWidth, bmInfo.bmHeight,
hMonoDC, 0, 0, PSDPxax ) ;
DeleteObject( SelectObject( hColorDC, hbrPat ) ) ;
hbmShadow = (HBITMAP)SelectObject( hMonoDC, (HGDIOBJ) hbmShadow ) ;
// select old bitmap into color DC
SelectObject( hColorDC, hbmOld ) ;
DeleteObject( (HGDIOBJ) hbmShadow ) ;
DeleteObject( (HGDIOBJ) hbmHighlight ) ;
ReleaseDC( NULL, hDC ) ;
return ( hbmResult ) ;
}
Download source code
|